The Partition Capacity Expansion of UDisk Greater Than 2TiB In Linux
In this example, if the disk capacity is greater than 2 TiB and cannot be partitioned by using the fdisk command, you can use the parted command to partition the disk. If the disk capacity of the udisk is greater than 2 TiB, you can use the following methods to partition and expand the capacity.
Note It is recommended that you do not partition the udisk on the uhost, so as not to affect the expansion of the udisk.
Before expanding the capacity of the disk, we recommend that you back up the data if there is data in the data disk.
Udisks can be expanded only when they are Available status. Since you need to unmount the udisk, your business will be interrupted, so please be cautious.
If you use the parted command to take effect in a timely manner, please confirm the operation before executing the command.
After the partition is completed, it needs to be formatted separately, otherwise it cannot be used directly.
Instructions
In this example, the
partedcommand is used as an example, and thepartedcommand cannot be used intersecting with thefdiskcommand. In this example, the udisk mount point is /dev/vdb. If you do not see the device, check the disk mount information and status.
Tips
-
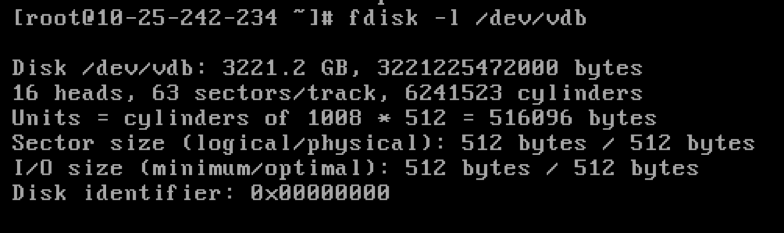
Create a big udisk and mount to uhost, and check the disk size
-
use
partedcommand to partition /dev/vdb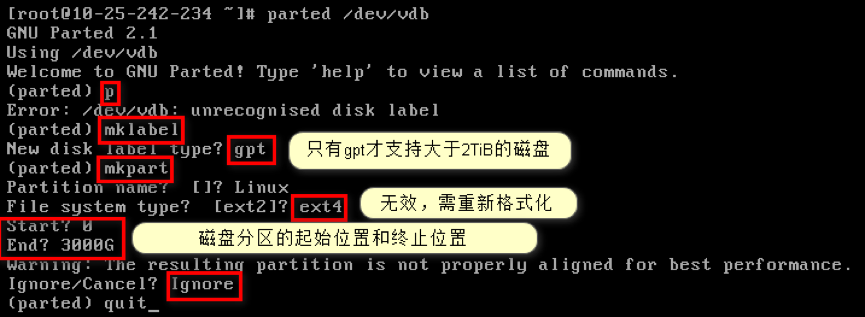
-
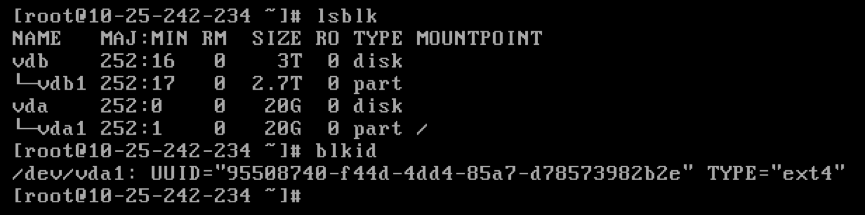
Check whether the disk partition is successful.
-
Format the corresponding disk partition.
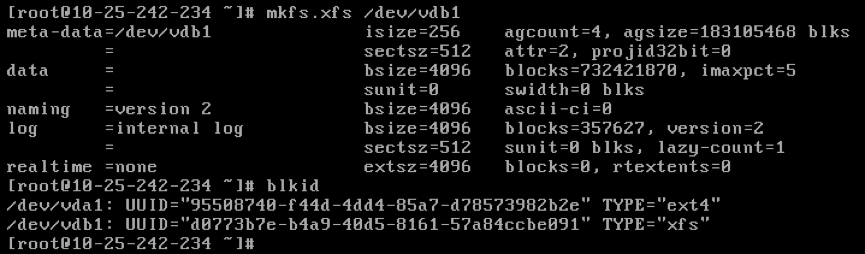
Note: This operation takes the
xfsfile system as an example. If you want to format it as anext4file system, please execute the commandmkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb1 -
Run the
mountcommand to mount the disk.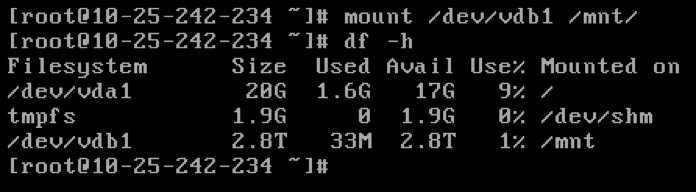
Now we begin to expand the udisk
-
View the current mount status, file system type, and partition status.
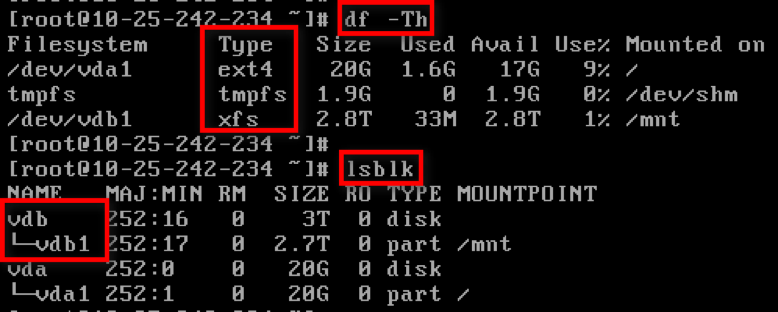
Note: The
lsblkcommand results show that there is partition(vdb1) in the VDB, and can be expanded according to the scheme described in this document. In other case, please see the partition expansion documentation. -
To unmount the udisk from the operating system and console, see Unmount UDisk. Use the console
Disk Managementtab to expand the udisk.
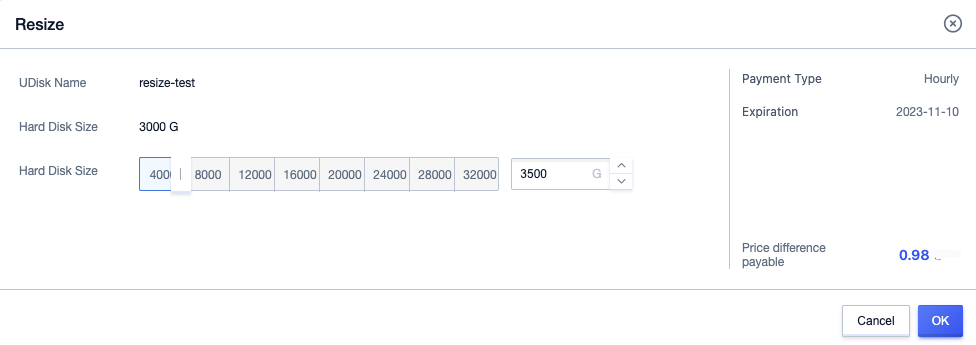
-
After expanding the udisk, mount the udisk to uhost Mount UDisk. After the mount is complete, check the disk size in the uhost.
fdisk -l /dev/vdb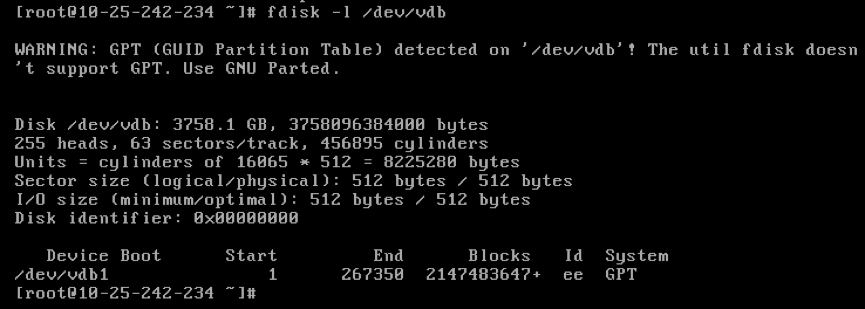
-
use
partedcommand to delete the original partition and create a new partition.parted /dev/vdb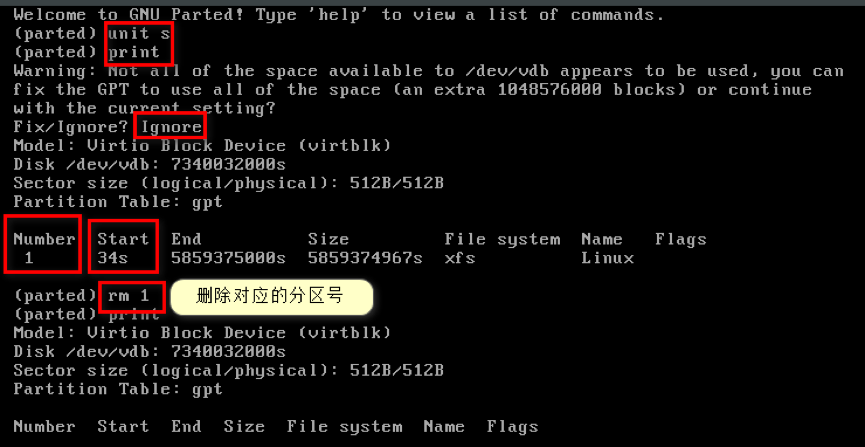
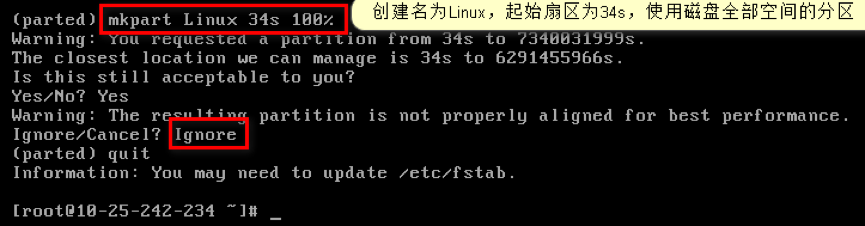
Note: Deleting a partition will not cause data loss in the data disk.
-
Check the file system and expand the capacity.
Note: The commands for checking and expanding capacity are different for different file systems, so please check the type of your file system and follow the corresponding steps.
xfs file system
- execute
xfs_repair /dev/vdb1command to check file systemxfs_repair /dev/vdb1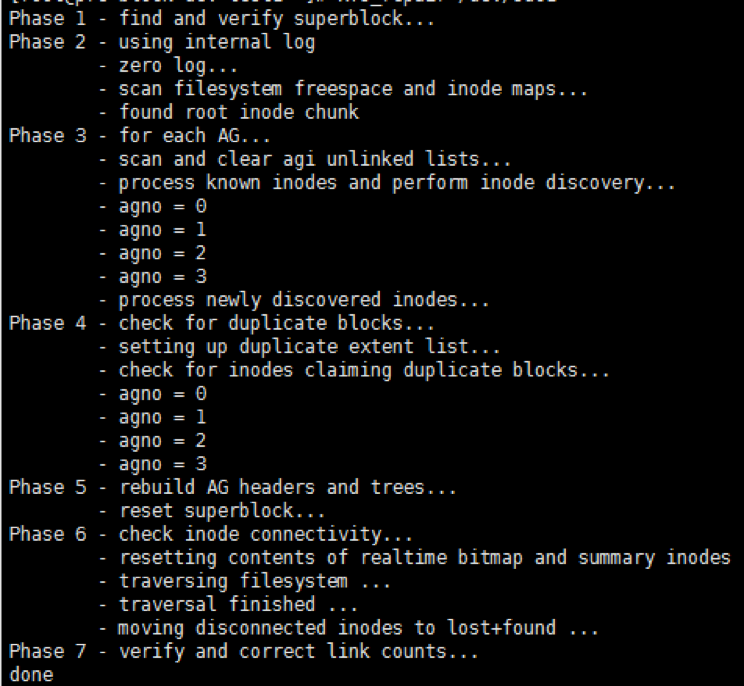
- execute
mountto mount udiskmount /dev/vdb1 /mnt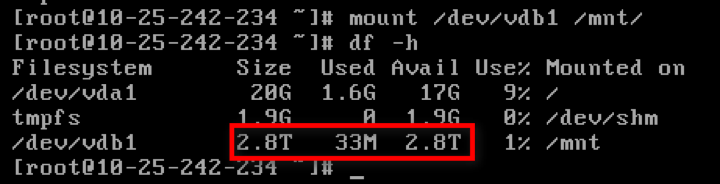
- execute
xfs_growfsto expandxfs_growfs /mnt/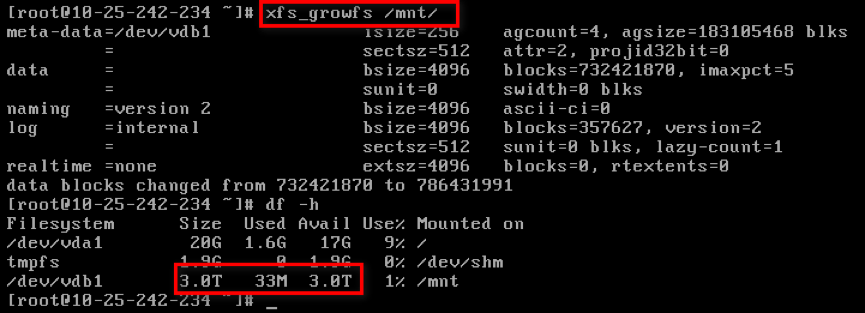
ext4 file system
- execute
e2fsck -f /dev/vdb1command to check the file systeme2fsck -f /dev/vdb1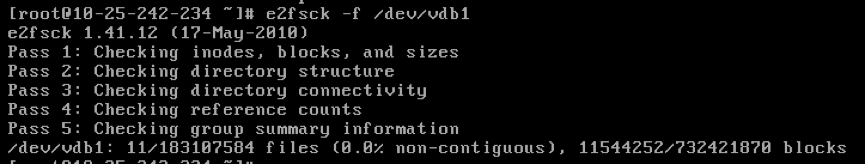
- execute
resize2fs /dev/vdb1command to expandresize2fs /dev/vdb1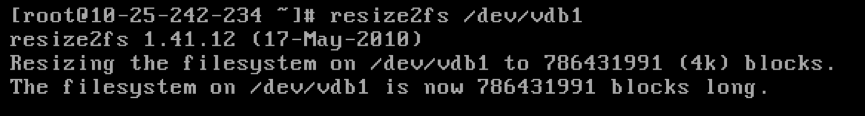
- execute
mountcommand to mount the diskmount /dev/vdb1 /mnt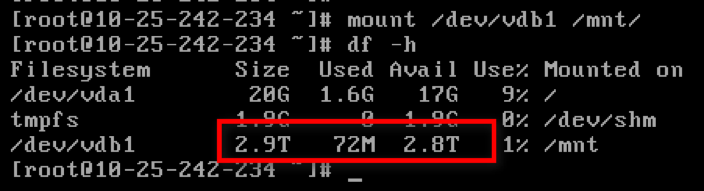
- execute