Linux
Notice:
Before formatting the disk, please confirm that if there is data in the data disk, it is recommended that you back up the data first.
It is recommended that you do not partition the cloud disk on the cloud host, so as not to affect the expansion of the cloud disk.
Operation instructions:
- Mount point of the data disk in this example:
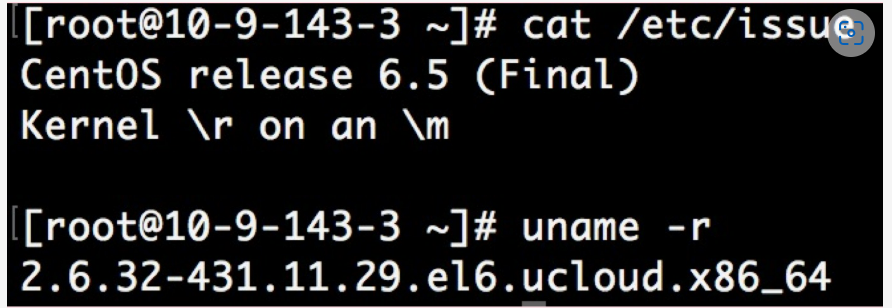
- The version of the environment applied in this example:
Specific operations:
- Connect to the host instance via the web console or an SSH tool. This example uses a self-owned SSH tool.
- After logging in to the host instance, use the fdisk -l command to view the hard disk partitions of the cloud host.
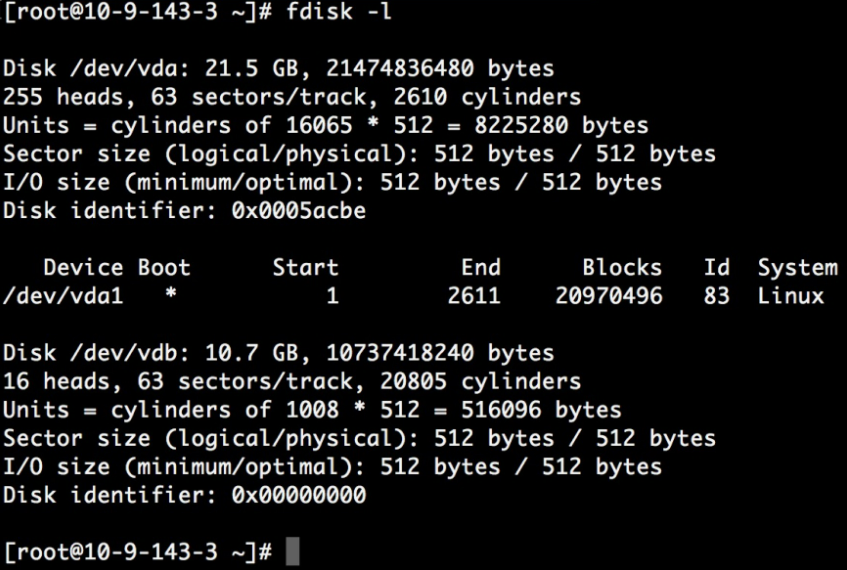
In this example, the cloud disk mount point is /dev/vdb. Please operate according to your actual situation. If the corresponding device is not found, please check the cloud disk mounting information and status.
- Create a file system using the command mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb.
This will format the existing data on the disk. Before performing this operation, please confirm that if there is data in the data disk, you should back up the data first.
In this example, the ext4 file system is used, and you can choose the required file system format by yourself.
- Check the execution result using the command parted /dev/vdb.
- Modify the /etc/fstab file to make the data disk mount automatically at system startup. Check UUID command. It is recommended to use UUID to configure the mounting information to avoid the potential disk symbol migration phenomenon in the Linux disk symbol allocation mechanism.
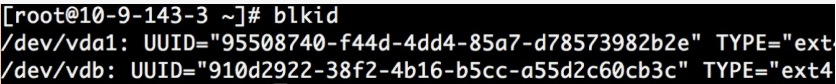
Use the command echo UUID=“910d2922-38f2-4b16-b5cc-a55d2c60cb3c” /mnt ext4 defaults 0 0 >> /etc/fstab.
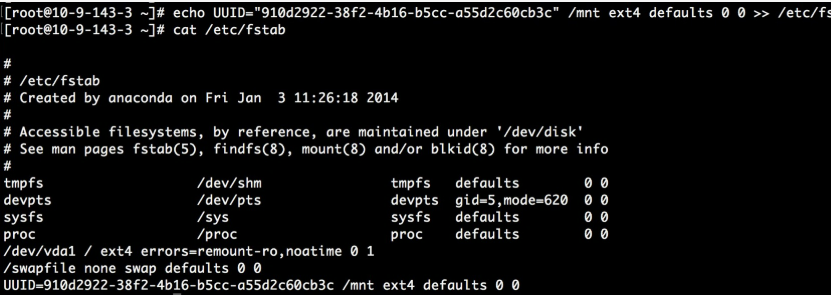
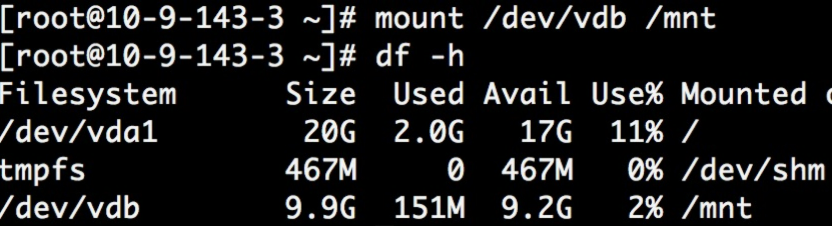
- Use the mount command to mount the disk.