Multi-Partition Data Disk_Linux
This operation example defaults to a data disk capacity of less than 2TiB. If the data disk capacity is greater than 2TiB, please refer to the chapter “Partition Expansion for Disks Larger Than 2TiB”.
If the host has multiple partitions created before, you can use the following method for expansion.
Notice:
It is recommended that you do not partition the cloud disk on the cloud host to avoid affecting the expansion of the cloud disk.
Before performing disk expansion, please confirm that if there is data in the data disk, it is recommended to back up the data first.
A cloud disk can only be expanded when it is in an available state. Since the cloud disk needs to be unmounted, your business will be interrupted, so please operate with caution.
Since the newly expanded space is appended to the end of the virtual disk, in multi-partition scenarios, only the last partition in sequence can be expanded.
Operational Notes:
- This example uses the fdisk command. The parted command cannot be used interchangeably with the fdisk command.
- In this example, the mount point of the cloud disk is /dev/vdb. Please operate according to your actual situation. If the corresponding device is not found, please check the mounting information and status of the cloud disk.
Specific operations:
- View the current mounting situation, file system type, and partition situation
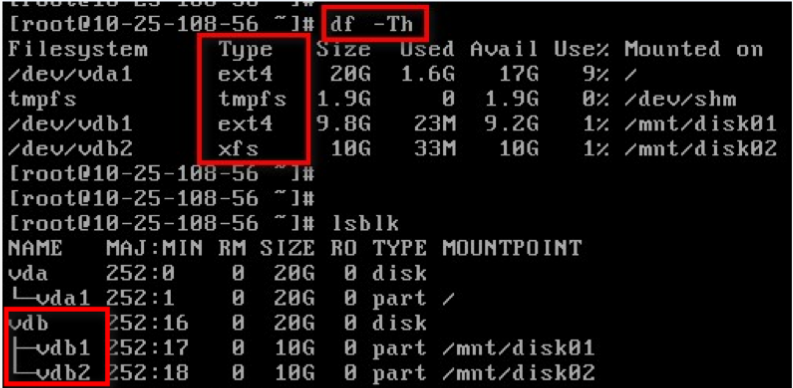
The result of the lsblk command shows that there are two partitions vdb1 and vdb2 under vdb, which are multi-partitions. You can expand them according to the solution described in this document. For other cases, please refer to the corresponding documents for expansion.
- Unmount the cloud disk in the operating system and console. For specific steps, see the chapter on unmounting cloud disks. Expand the cloud disk via the cloud disk console.
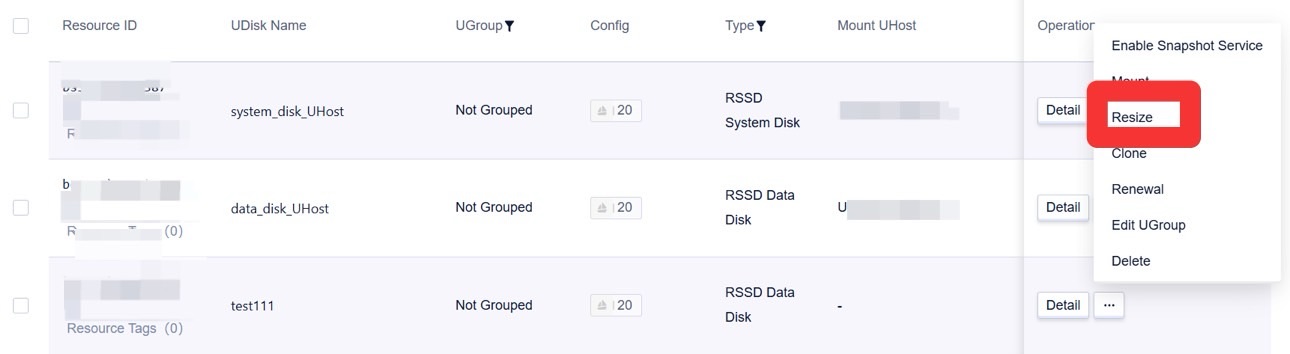
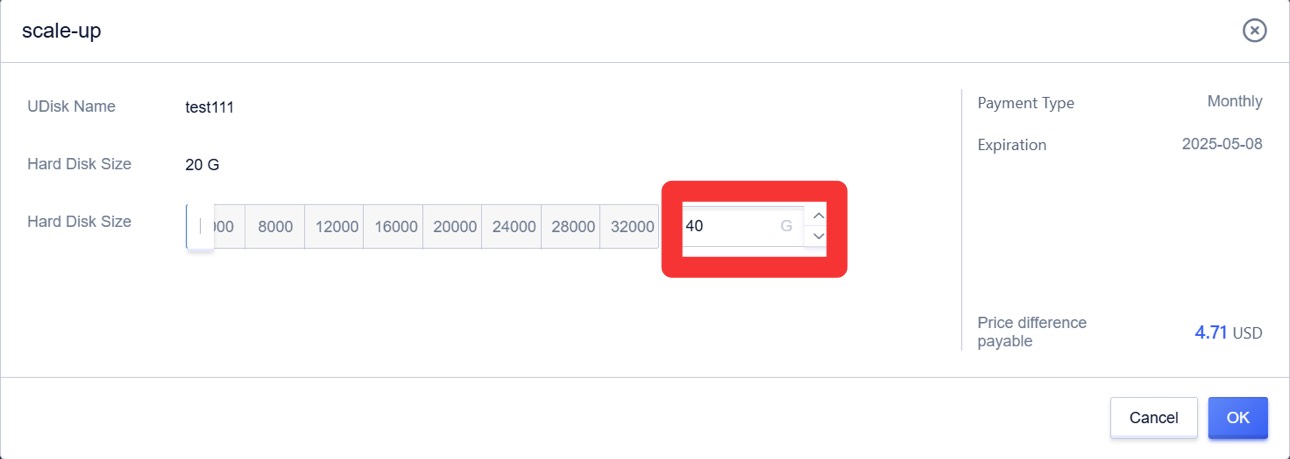
- Mount the cloud disk in the console. For specific steps, see the chapter on mounting cloud disks. After mounting is completed, check the disk size in the operating system.
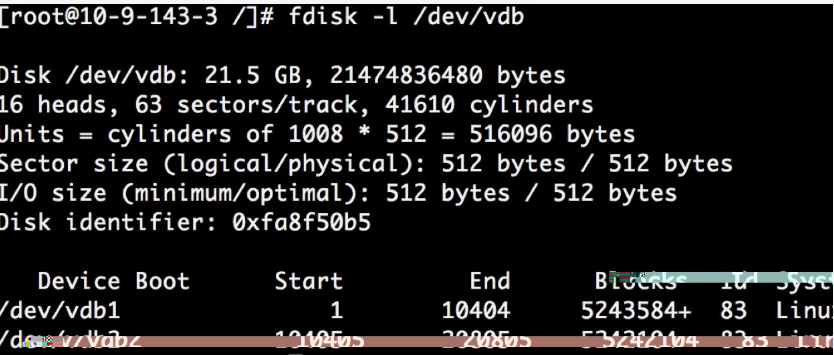
- Use the fdisk command to delete the second partition (/dev/vdb2) and create a new partition.
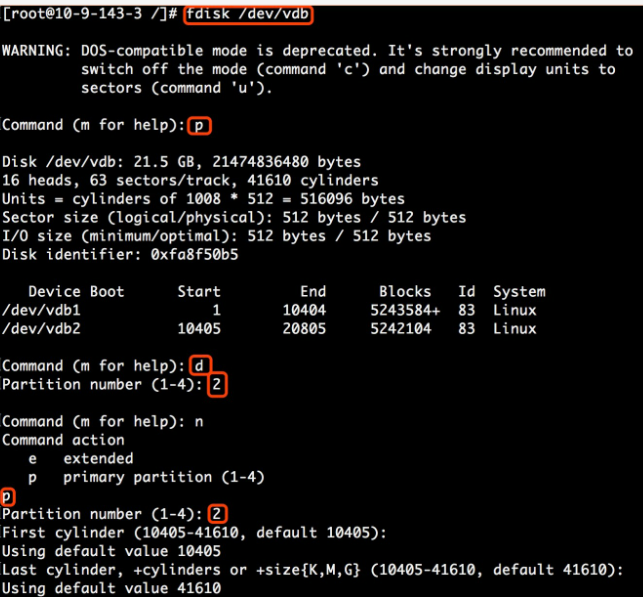
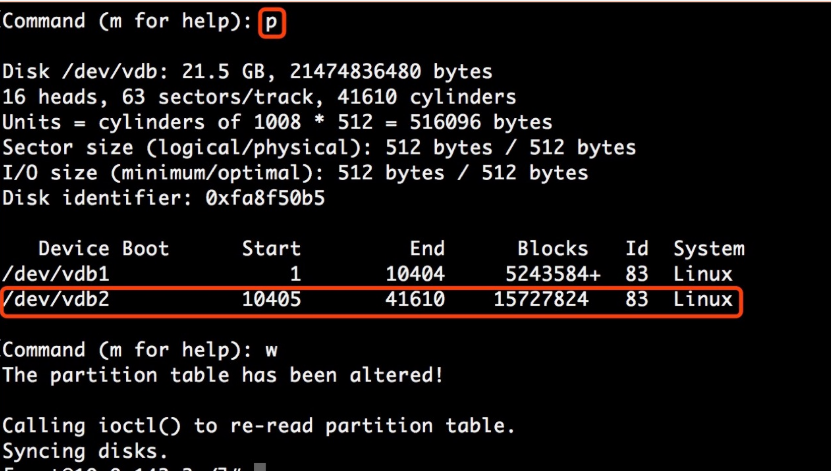
Note: Deleting the partition will not cause the loss of data on the data disk.
- Check the file system and expand it.
Note: Under different file systems, the commands to check and expand are different. Please confirm your file system type and operate according to the corresponding operation steps.
ext file system
- Execute e2fsck -f /dev/vdb2 and resize2fs /dev/vdb2 to check and expand operations respectively.
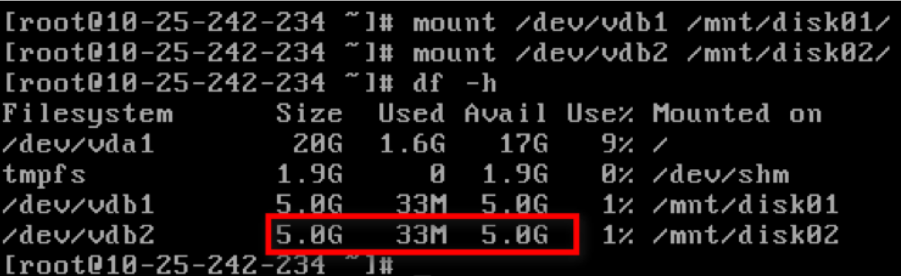
- Use the mount command to remount the disk.
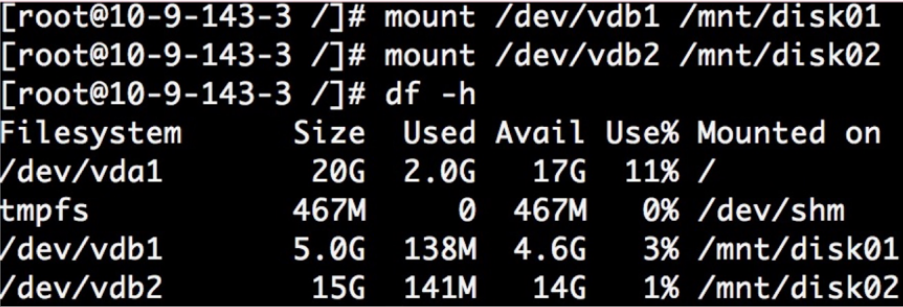
xfs file system
- Execute xfs_repair /dev/vdb2 to check the file system.
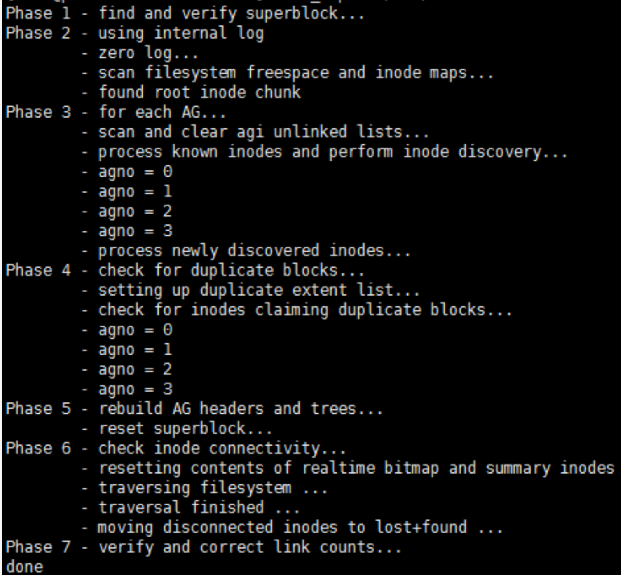
- Use the mount command to remount the disk.
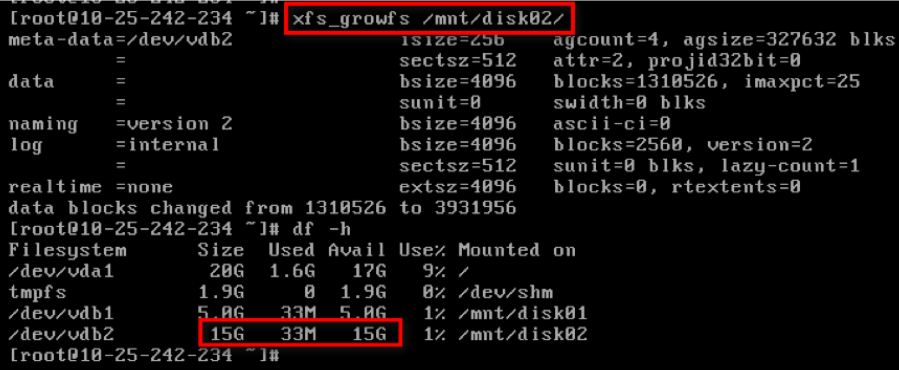
- Execute xfs_growfs command to expand.