Application Scenarios
The core function of DNS is to translate domain names into IP addresses, thus eliminating the dependence of services on IP addresses. The following functions can be realized through domain name operations:
Service Discovery
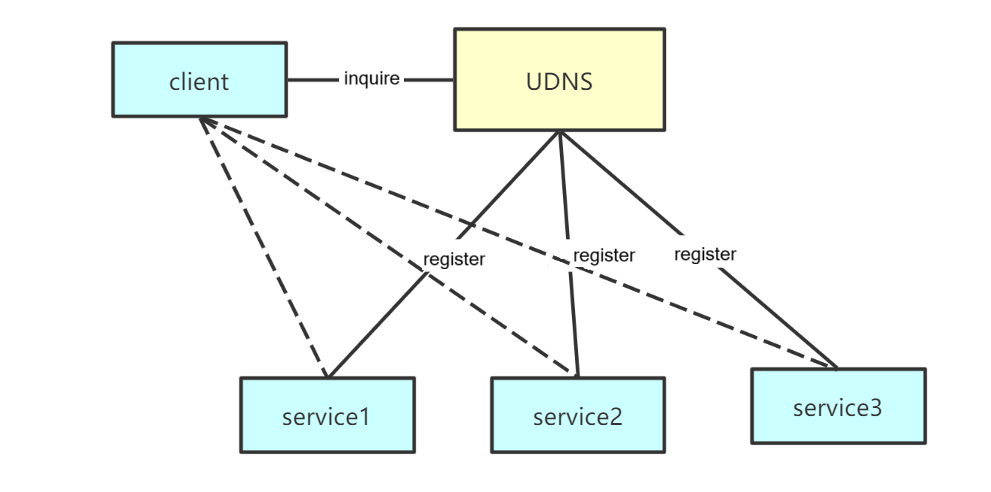
As shown in the picture above, the client takes the domain name as the service request object. The services respectively register the corresponding domain names in the UDNS system, so that the client can access the services through the domain name. When the service IP address migrates, the client’s configuration does not need to be changed. Modifying the DNS resolution record in UDNS can seamlessly switch the service address.
Load Balancing
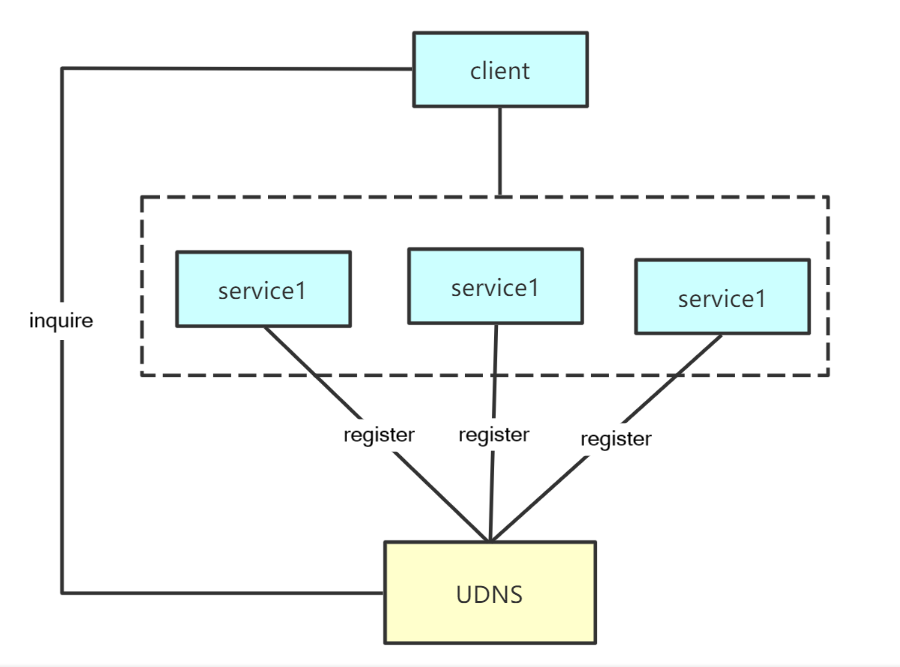
As shown in the picture above, UDNS supports the “Random Answer” mode. Users can configure the A records and AAAA records in this mode. UDNS can randomly return the corresponding values based on the configured record values and weights. According to the weights, client requests are allocated to various services.
High Availability
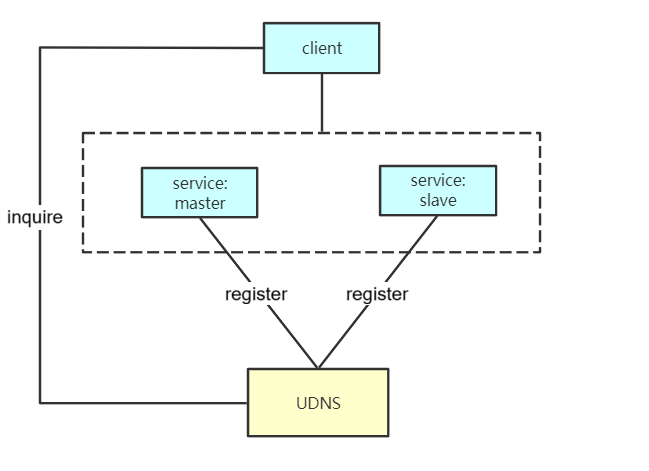
As shown in the picture above, clients can achieve high availability of services by pre-registering master records.